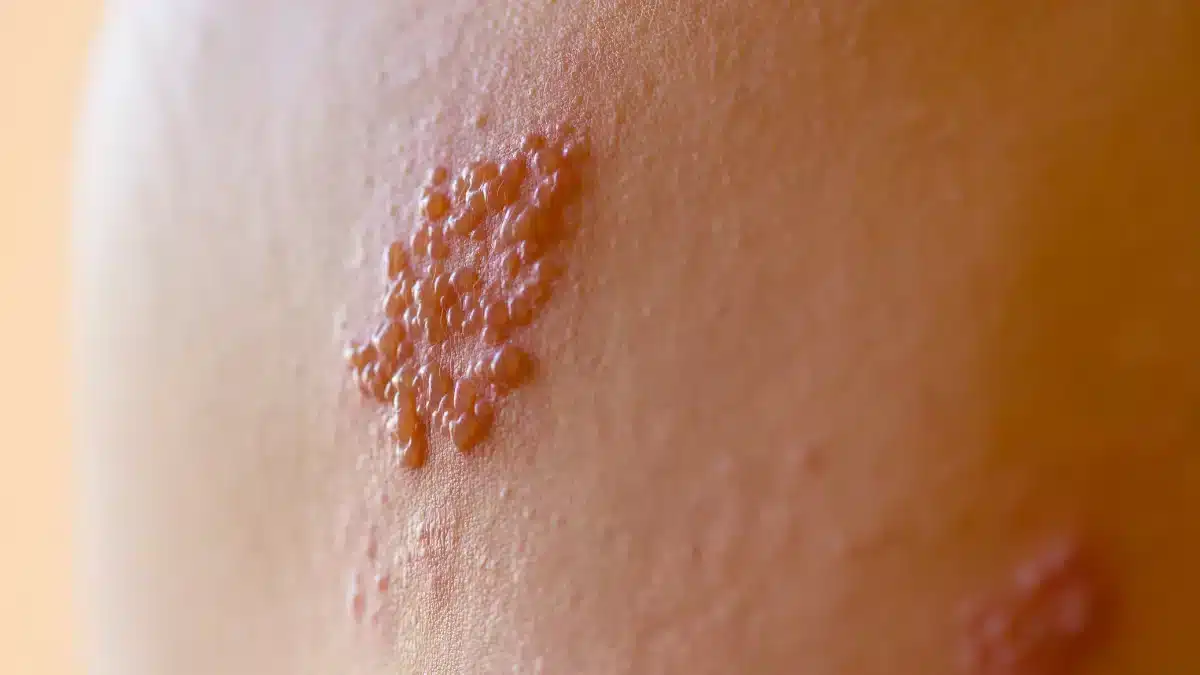
Genital Herpes Treatment: A Comprehensive Guide
Genital Herpes is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) caused by the Herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or type 2.
It leads to the development of painful blisters on the genitals and surrounding areas.
The condition is typically transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
While symptoms can clear up on their own, they might resurface.
The CDC approximated that within a single year, there were 572,000 newly reported cases of Genital Herpes infections in the United States.
Although there is no cure for Genital Herpes, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms.
Read this insightful article to learn more about Genital Herpes treatment.
Diagnosis of Genital Herpes
Healthcare providers usually diagnose Genital Herpes through a physical examination and an assessment of sexual activity history.
To confirm the diagnosis, the healthcare provider may take a sample from an active sore and perform one or more tests to see if the Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) is present.
Virologic tests
Virologic tests play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing Genital Herpes. The primary tests include:
- In the context of Genital Herpes, virologic tests confirm the diagnosis of HSV-1 or HSV-2 infection
- These tests include viral culture, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and type-specific serologic tests
- Virologic tests are crucial for confirming the presence of the Herpes simplex virus and differentiating between HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections
Type-specific serologic tests
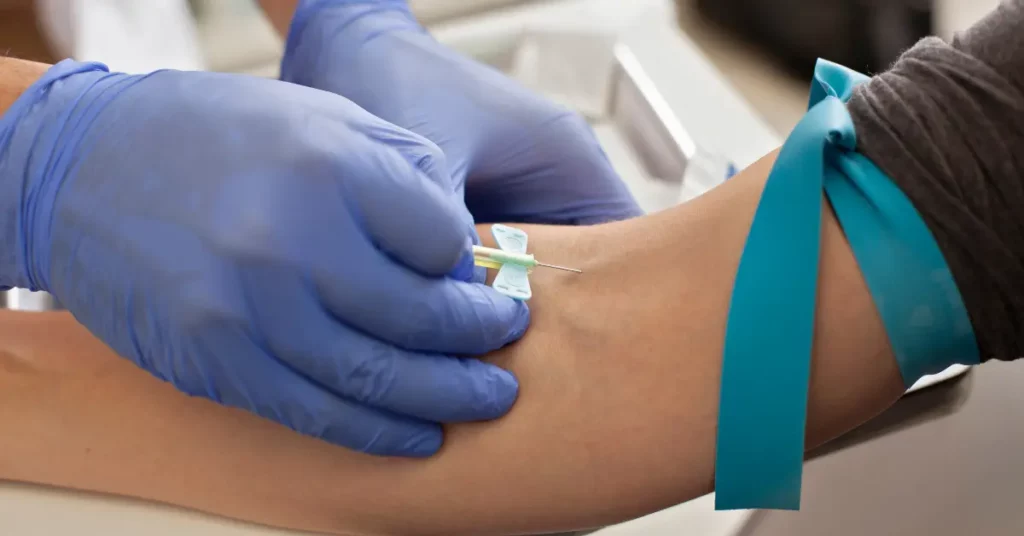
Following are the Type-specific serologic tests that can be done to diagnose and understand Genital Herpes infections.
- Type-specific serologic tests (TSS) are used to differentiate between HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections
- TSS can detect antibodies to HSV infection typically six weeks to 3 months after infection
- Some of the type-specific serologic tests for Genital Herpes include HerpeSelect and Biokit HSV-2 Rapid Test and HSV-1 and HSV-2 Western Blot test
- These tests can be particularly useful when direct methods, such as viral culture or PCR testing, are not sufficient or when genital lesions are not present
Treatment for Genital Herpes
Genital Herpes has no cure; treatment focuses on symptom management and minimizing the frequency and intensity of outbreaks.
Antiviral medications are commonly prescribed for Genital Herpes treatment.
The types of Antiviral drugs used for this purpose are:
Acyclovir (Zovirax)
Here are the ways Acyclovir can assist in managing Genital Herpes:
- Acyclovir is one of the first Antiviral medications used to treat Herpes infections
- It is available in oral, topical, and intravenous forms
- The oral form is commonly prescribed for Genital Herpes
- Alongside oral forms, Acyclovir is accessible in topical versions like creams or ointments
- These topical preparations are applied directly to the affected skin, offering localized relief and helping to speed up the healing of lesions
Valacyclovir (Valtrex)
Ways Valacyclovir can help manage Genital Herpes:
- Valacyclovir is a prodrug that undergoes conversion into Acyclovir within the body
- It is often preferred by some individuals due to its more convenient dosing schedule
- Valacyclovir is typically taken less frequently than Acyclovir, which can enhance patient adherence to the prescribed treatment plan
- The convenience of less frequent dosing may be particularly beneficial for individuals who need long-term suppressive therapy
Famciclovir (Famvir)
Following are the ways Famciclovir can help you manage Genital Herpes:
- Similar to Acyclovir and Valacyclovir, Famciclovir is another antiviral medication used to treat Herpes infections
- Like other antiviral medications for Herpes, Famciclovir is most effective when initiated early in the course of an outbreak
- Early initiation, ideally at the first signs or symptoms of a recurrence, can lead to better outcomes, including a reduction in the duration and severity of symptoms
Prevention

Prevention for Genital Herpes includes various measures to reduce the risk of transmission.
Here are some key preventions you can apply:
- Condom Use: The consistent and proper use of condoms can lower the risk of contracting Genital Herpes
- Avoiding Sexual Contact During Outbreaks: It’s important to avoid sexual contact during outbreaks when sores are present, as this is when the risk of transmission is highest
- Open Communication: Effective communication is vital. Being open and honest with sexual partners about herpes, including disclosing the infection and discussing preventive measures, is crucial
- Hand Hygiene: Washing hands with soap and water after any possible contact with sores can help reduce the risk of spreading the virus
- Antiviral Medication: For individuals with Genital Herpes, taking antiviral medication daily (suppressive therapy) can help reduce the risk of passing the infection to a partner
- Recognizing Symptoms: Being alert to the symptoms that signal an outbreak is coming can help individuals avoid sexual contact during these times
Conclusion
Genital Herpes, resulting from the herpes simplex virus, is a common Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) characterized by recurrent symptoms.
Diagnosis involves physical exams and virologic tests to confirm HSV infection.
While there is no cure, antiviral medications like Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Famciclovir effectively manage symptoms and reduce outbreaks.
Early initiation of treatment is crucial for optimal results.
Prevention includes safe practices such as condom use, open communication with partners, and abstaining during outbreaks.
Despite the absence of a cure, a proactive approach to treatment and prevention empowers individuals to lead fulfilling lives while managing Genital Herpes.
Regular communication with healthcare providers is key for personalized care and effective management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Genital Herpes deadly?
Herpes is not life-threatening and typically doesn’t lead to severe health issues. While initial outbreaks can be bothersome and painful, they tend to be the most intense. Over time, outbreaks often decrease in frequency and may cease altogether for many individuals.
Can I kiss someone with Genital Herpes?
Kissing someone with Genital Herpes carries a risk of transmission, as Herpes spreads through skin-to-skin contact and saliva. Oral Herpes can also be contracted through oral sex or sharing objects in contact with an infected person’s saliva. Caution and communication can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Is it safe to touch Genital Herpes?
Genital sores carry the Herpes virus and can be transmitted to others through sexual contact. Additionally, direct contact with the sores and subsequent contact with other body parts can spread the infection within the individual’s body.
What is the treatment for Genital Herpes?
Antiviral medications like Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Famciclovir are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms and reduce outbreaks. While there’s no cure, these medications help alleviate discomfort and may be used for both episodic and suppressive therapy.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trustworthy.