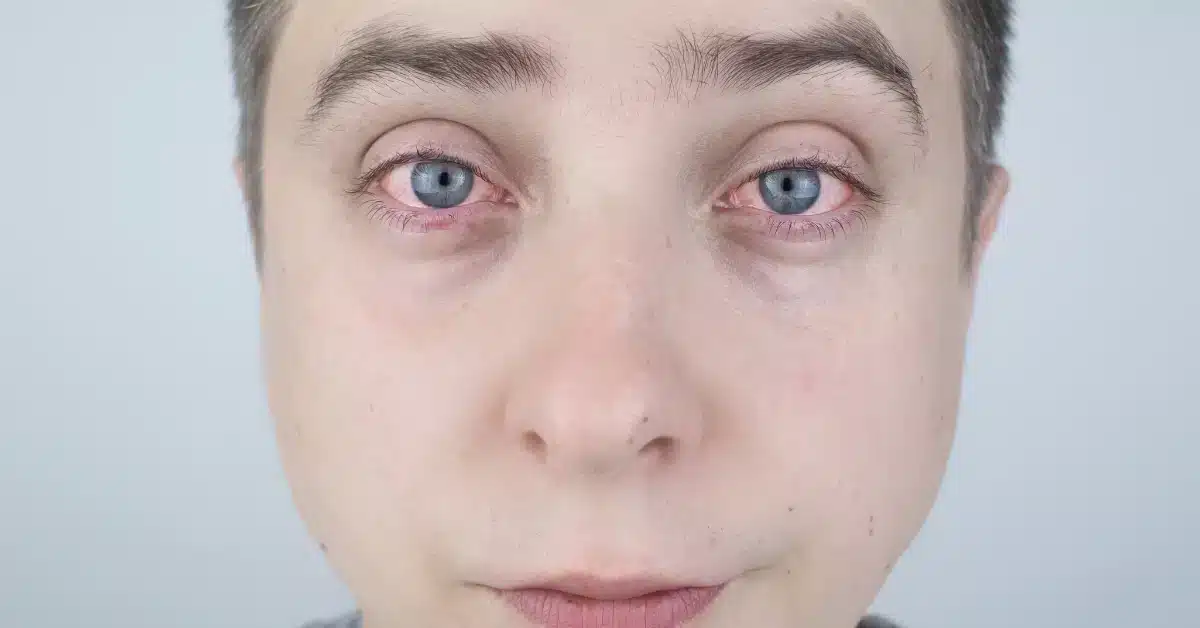
Episcleritis vs Scleritis: Understanding the Differences and Similarities
Episcleritis and Scleritis are both inflammatory conditions affecting the eyes.
Scleritis affects the sclera, the outermost eye layer. In comparison, Episcleritis affects the tissues between the conjunctiva and sclera.
They can even cause redness, but Scleritis can be a rarer and more severe condition.
Episcleritis is a common or mild inflammation that occurs due to unknown reasons.
A 2013 study estimated the incidence of episcleritis as 41.0 per 100,000 per year and prevalence at 52.6.
The incidence of scleritis was 3.4 per 100,000 person-years. The annual prevalence ratio of 5.2 per 100,000 persons.
This study found that patients with scleritis were older than those with episcleritis.
Also, women had higher rates of both episcleritis and scleritis than men.
An overview: Episcleritis vs Scleritis
Some of the fundamental differences between Episcleritis and Scleritis are as follows:
| Scleritis | Episcleritis | |
|---|---|---|
| Pathophysiology | Autoimmune disorder | Idiopathic inflammation |
| Types | Anterior Scleritis Posterior Uveitis | Nodular Episcleritis Simple Episcleritis |
| Symptoms | Severe Pain Pain while moving the eye Blurred vision Photophobia Subacute onset | Mild pain Redness Irritation Acute onset |
| Physical Examination | It doesn’t blanch with phenylephrine drops Adherent vessels Bluish hue Systematic inflammation (Joint pain, rashes, etc.) Slit lamp may reveal nodules, corneal changes and thinning of the sclera | Blanch with phenylephrine drops Mobile vessels Reddish hue |
| Treatment | Systematic steroids NSAIDs Topical antibiotics | Consider topical steroids in obstinate cases Self-limited |
Continue reading to know more detailed information about Episcleritis vs Scleritis.
Types
Scleritis and Episcleritis have two types depending on the area of the inflammation in the eye.
Types of Scleritis

Scleritis is divided into Anterior Scleritis and Posterior Uveitis.
Anterior scleritis is when the front of the sclera is inflamed. It is the most common type of scleritis.
Posterior uveitis is when the back of the sclera is inflamed.
It is less common but can lead to serious eye problems like glaucoma.
Types of Episcleritis
Episcleritis is divided into Nodular Episcleritis and Simple Episcleritis.
Nodular Episcleritis is a discrete, raised area of inflamed episcleral tissue.
Simple Episcleritis is vascular congestion in the absence of an obvious nodule.
Sometimes, the disorder may occur because of some unknown causes.
Symptoms
Some of the symptoms you can look out for to differentiate between Episcleritis and Scleritis are as follows:
Episcleritis
In Episcleritis, patients may face minor pain in the eye. There may be some redness and irritation on the white part of the eye.
Generally, Episcleritis patients only complain about discomfort or irritation in the eye.
Episcleritis may be present with epiphora but does not result in reduced acuity.
Scleritis
This condition can lead to other severe conditions affecting vision.
The connection between the optic nerve’s dural and arachnoid sheaths may decrease vision and cause inflammation.
Some of the other symptoms may include increased lacrimation and photophobia.
Patients having scleritis may face more pain than Episcleritis. The pain may get transferred to the face, cheek, or jaw from the eyes.
The pain may increase at night and worsens with eye movement.
Also Read: Want to learn what causes Scleritis? Read our informative article, “Most Common Cause of Scleritis“.
Clinical indications
Both conditions have slightly different indications:
Episcleritis
It is generally a mild inflammation of the eyes that may resolve within days or weeks.
Nodular Episcleritis is more painful than simple Episcleritis.
Because of the involvement of conjunctival and episcleral plexi, the affected area may appear red.
There may be increased intraocular pressure due to increased episcleral venous pressure.
Also Read: Do you know why Episcleritis happens? Read “Episcleritis Causes: Know the Triggers” to find out the answer.
Scleritis
It consists of severe pain in the eye. A bluish hue with scleral edema and some dilatation may characterize it.
Other indications may depend upon the location of the disease and its severity.
In the case of Anterior Scleritis, it may be associated with thinning of the cornea and uveitis.
Treatments
The treatment may differ for both conditions depending on the underlying disease or condition causing them.
Treatment for Episcleritis

Episcleritis can be an uncomfortable condition. Moreover, its symptoms also consist of mild pain.
The treatment for Episcleritis focuses on reducing the symptoms with the help of lubricating eye drops.
Severe cases may be treated using topical or oral anti-inflammatory medicines.
- Artificial tears may help in relieving in case of nodular episcleritis. Your doctor may recommend Eyemist E/D 10ml as artificial tears.
- The doctor may suggest topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) drugs for more symptomatic patients.
Topical NSAIDs may reduce mild pain and inflammation without changing intraocular pressure. Those NSAIDs may include NS Aid 5ml eyedrop. - Oral NSAIDs may also help in nodular episcleritis.
- In severe conditions, your doctor may prescribe a short course of topical steroids.
Treatment of Scleritis
If someone has symptoms of Scleritis, they must contact their eye specialist.
Scleritis is a rare and severe condition as compared to Episcleritis.
- Treatment of Scleritis depends on its type and on whether the cause is an underlying disease.
- You can use medications like oral NSAIDs and prednisolone.
- Anterior scleritis can be managed using systemic steroids and may sometimes need surgery.
- In case of infectious scleritis, antibiotics and immunosuppressants must be used with proper care.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Scleritis and Episcleritis are conditions that can cause inflammation of the eye.
Scleritis is a more serious condition that can cause severe eye pain and vision loss and may lead to other complications.
At the same time, Episcleritis is a milder form of eye inflammation that typically resolves on its own or with minimal treatment.
Treatment options for both conditions may include eye drops, oral medications, or in some cases, surgery.
Although Scleritis and Episcleritis share some similarities.
They are distinct conditions that require different approaches to diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Episcleritis progress to Scleritis?
Only in the case of Herpes zoster does Episcleritis progress to scleritis. The condition starts as Episcleritis, the vascular stage of the eruption. This then appears after three months as Scleritis in the same site.
Which is more painful, Scleritis or Episcleritis?
Scleritis is considered more painful. It causes deep or boring kind of pain around the eye. The pain may transfer from your eyes to your jaw, face, or cheek.
What is the most common cause of Episcleritis?
Episcleritis is often an idiopathic condition. But it is sometimes associated with autoimmune diseases, infections, and systemic collagen vascular disease.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trustworthy.