Beyond the Basics: A Comprehensive Guide to Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) largely overlooked due to its asymptomatic nature, but it poses a major challenge to global health.
According to the WHO, in 2020, Gonorrhea ranked second among bacteria-caused curable STIs affecting 82.4 million people.
It can be observed in all age groups, but the sexually active ones are at a higher risk.
The chances of getting Gonorrhea increase due to the lack of awareness about it.
So, it becomes even more vital to know about it if you wish to protect yourself from such unwanted troubles and enjoy a healthy, intimate life.
This article provides detailed information about Gonorrhea, covering causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
What is Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a Sexually Transmitted Infection that often spreads through oral, anal, or vaginal sex. It is caused by the bacterium Neisseria Gonorrhoeae.
Other names like the clap and drip know gonorrhea.
The word “clap” comes from the French term “clapier,” which means brothel. Back then, it was used to talk about places where people engaged in prostitution.
Gonorrhea was often caught in these places, so the term “clap” was linked to the infection.
The word ‘drip’ is used to describe the condition as the visible symptom of Gonorrhea is discharge dripping from the penis.
Types of Gonorrhea

Gonorrhea is classified into three types:
Extragenital Gonorrhea,
Extragenital Gonorrhea targets areas outside the genital region. These may involve the rectum or pharynx, causing pain, discomfort, and sometimes bleeding.
The most frequent cases of Extragenital Gonorrhea are when two men are involved in sexual activity.
Urogenital Gonorrhea
Urogenital Gonorrhea is most likely to occur and affect urinary and genital organs. It affects urethritis in men and cervicitis in women.
Untreated Urogenital Gonorrhea poses a risk of reproductive complications in women if it travels to the upper urogenital tract.
Some of these problems can be infertility, endometriosis, and ectopic pregnancy.
Disseminated Gonococcal infection
Disseminated Gonococcal Infection is also known as DGI. It is rare but may occur if Gonorrhea goes untreated.
In DGI, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae reaches the bloodstream and affects distant body parts.
DGI might cause Septic Arthritis, Tenosynovitis (inflammation of tendons), pustular skin lesions, and Arthralgias.
Other subtypes of Gonorrhea
There are several subcategories of Gonorrhea, which involve Oral Gonorrhea, Gonococcal Conjunctivitis, Super Gonorrhea, Phrangeal Gonorrhea and Anorectal Gonorrhea.
Super Gonorrhea is drug-resistant Gonorrhea, which not only resists current treatment but other drugs like Penicillin, Macrolides, etc.
Gonorrhea symptoms
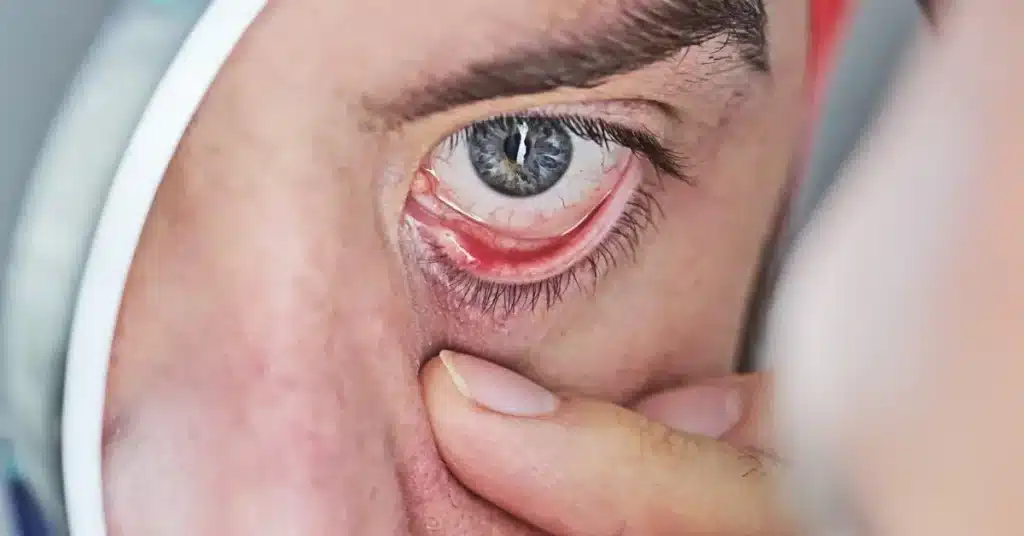
Gonorrhea symptoms can be tricky to figure out. This infection may or may not show symptoms.
Both men and women can have symptomatic and asymptomatic Gonorrhea.
However, women are more likely to have asymptomatic Gonorrhea.
The symptoms may take two days to 2 weeks to show up. In some cases, it might take months.
Since the symptoms may not appear for a vast span, the chances of the infection going untreated increase.
So, recognizing the minimal symptoms, even if they are vague, becomes even more vital.
Some of the common symptoms are:
- Throat: Swelling in the lymph nodes, inflammation or redness and sore throat
- Rectum: Bleeding, itching, painful bowel movement, and pus discharge
- Eyes: Pain, discharge from the eyes and sensitivity to light. Eyelid swelling, redness, or tenderness might also be observed
- Joints: If the infection affects joints, it may lead to septic arthritis
There are a few symptoms that are gender specific. These impact the genital area and urinary organs.
Gonorrhea symptoms male
Penile Gonorrhea affects the penis or related areas.
Hence, people assigned male at birth are likely to experience the symptoms mentioned below in the case of Gonorrhea.
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Frequent urination or the urge to pee
- Discharge from the tip of the penis (green, yellow, or white)
- Swelling at the opening of the penis
- Swelling of testicles
- Testicular pain
Gonorrhea symptoms female
Females suffering from Gonorrhea may experience:
- Vaginal discharge of greenish or cream in color or watery
- Painful sex
- Pain while urinating
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Lower abdominal pain
- Increased flow during periods
- Spotting in between periods
Gonorrhea Causes
The cause of Gonorrhea is the bacterium Neisseria Gonorrhoeae.
This bacteria invades the mucous membrane of body parts like the eyes, rectum, mouth, and reproductive tract to spread the infection.
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae infections, if left untreated, are known to be responsible for several complications.
Some of these can be infertility, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, and scrotal swelling.
People aged 15 to 49 years are highly prone to Neisseria Gonorrhoeae infections.
Gonorrhea transmission

Being a Sexually Transmitted Infection, it transfers from sexual contact. It can be oral, anal, or vaginal.
However, sometimes, it passes from infected mother to child during pregnancy.
Gonorrhea infection can be transmitted by coming in contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person.
Contact like kissing may also spread the infection, especially throat Gonorrhea.
Casual kissing alone rarely leads to transmission.
However, engaging in deep kissing with tongue involvement or kissing between sexual activities can increase the risk of spreading the infection.
Risk factors
It is essential to understand that certain practices increase the chances of getting Gonorrhea.
One must avoid the following to eliminate unwanted issues.
- Having unprotected sex
- Multiple sex partners
- Having a partner with several sex partners or a history of casual hookups without protection
- Sexual contact with a person having Gonorrhea
Other risk factors include:
- Having another STD and a compromised immune system
- If you had a history of Gonorrhea (treated)
- Pregnancy when affected by Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea diagnosis
To diagnose if a person has Gonorrhea, some tests can be helpful in case of both symptomatic and asymptomatic Gonorrhea. After examining your problem, a doctor will suggest the right test.
These may include:
- Urine test: A urine sample is collected to check for infection. It is mostly helpful in case of Urogenital Gonorrhea
- Extragenital screening: A swab of the throat or rectum is used for lab testing to check for bacteria in case of oral and rectal gonorrhea when urine test fails.
- Swab: Besides extra genital screening, swabs can also be used to check for infections in genital areas
Gonorrhea treatment
Gonorrhea will not go away without treatment. If left untreated, it may prove to be fatal.
That should not be a cause to worry as the right treatment to cure Gonorrhea in most cases.
The most common medication used to treat Gonorrhea is antibiotics.
The CDC recommends a single 500 mg intramuscular dose of Ceftriaxone, given as a shot.
However, emerging drug-resistant strains raise concerns, making prompt and accurate treatment crucial.
While medication halts the infection, it may not reverse any permanent damage.
Individuals receiving treatment should abstain from sexual activity for at least seven days.
A follow-up test-of-cure is unnecessary for genital and rectal infections but is vital for throat infections 7-14 days post-treatment.
To prevent reinfection, both men and women should undergo retesting three months after the initial treatment.
Equally important is ensuring that sexual partners from the last 60 days also receive screening and treatment to break the chain of transmission.
Untreated Gonorrhea
Normally, Gonorrhea does not cause complications, but untreated Gonorrhea can.
Such cases arise due to asymptomatic Gonorrhea, as it is hard to detect.
Moreover, if the incubation period (period between acquiring infection and the onset of symptoms) stretches for long, it delays treatment of Gonorrhea and complications may arise.
Some of them can be:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
- Increased risk of HIV
- Epididymitis (inflammation of the tubes that carry semen)
- Disseminated Gonococcal Infection (infection enters bloodstream)
- Infertility in men and women
- Complications in childbirth
- Gonococcal Conjunctivitis
Gonorrhea prevention
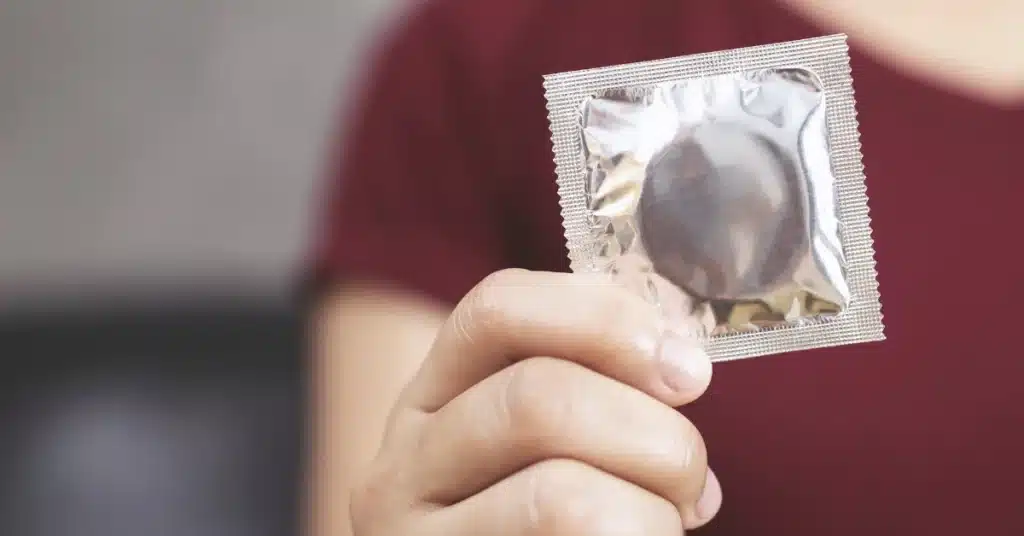

It is vital to lay an equal emphasis on prevention if not more than cure.
One must take adequate steps to protect oneself and the partner from unwanted problems.
Some of these can be:
- Practicing abstinence, if possible
- Using protection while having sex, like condoms and dental dams
- Not hiding STI history from partner
- Getting annual check-ups for Gonorrhea
- Using proper medication and undergoing treatment as per the doctor
- Avoiding having multiple sex partners
- Avoiding having sex with a person infected by Gonorrhea
Conclusion
Gonorrhea, caused by the bacterium Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) affecting all genders.
It spreads through sexual contact and may lead to severe complications if untreated.
Symptoms can include painful urination, genital discharge, and, in rare cases, joint inflammation.
Testing involves urine samples and swabs, with antibiotic treatments like Ceftriaxone being common.
Effective treatments for Gonorrhea typically involve antibiotics such as Ceftriaxone or Cefixime, administered under medical guidance.
Untreated Gonorrhea can result in Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, HIV susceptibility, and infertility.
Prevention includes safe sex practices, regular check-ups, and communication about STI history with partners.
Seeking professional medical care is crucial, as consulting a healthcare professional ensures proper treatment for Gonorrhea.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do most people get Gonorrhea?
Most people get Gonorrhea from sexual contact with an infected person. It may involve anal, vaginal, and oral sex. The risk increases without the use of protection. Ejaculation is not mandatory for the infection to spread. If the mother is infected, it can pass to the child during childbirth.
Can Gonorrhea spread from kissing?
Casual kissing may not be a concern, but deep kissing may spread the infection. This may happen if the bodily fluids of an infected person come in contact with the mouth. Then, you might end up with Oral Gonorrhea. Although such cases are rare.
Does Gonorrhea spread from breastfeeding?
Several STDs and STIs like HIV spread from breastfeeding. However, until now, no research has found a link between Gonorrhea and breastfeeding. Thus, Gonorrhea is unlikely to affect your child through breastfeeding. So you can continue to breastfeed after consulting your doctor.
Does sperm carry Gonorrhea?
One of the most common means of spread of Gonorrhea is bodily secretions. Semen and precum carry the infection. This may be passed on to the partner during sexual contact (including oral sex). Complete penetration of the penis in the vaginal or anal canal is not mandatory for spreading Gonorrhea.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trus






