Understanding Genital Herpes: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
As a widely spread STI, genital Herpes poses significant public health concerns.
It is a highly contagious condition caused by Herpes Simplex Virus and may have serious consequences for affected individuals.
Beyond the physical discomfort caused by outbreaks, genital Herpes can also impact an individual’s emotional well-being.
This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the virus and its treatment and prevention strategies.
In this article, we will explore genital Herpes in detail, covering its symptoms, causes, treatment, and preventive steps.
Symptoms of genital Herpes
This section has discussed genital Herpes symptoms in detail as per the published research of the National Library of Medicine.
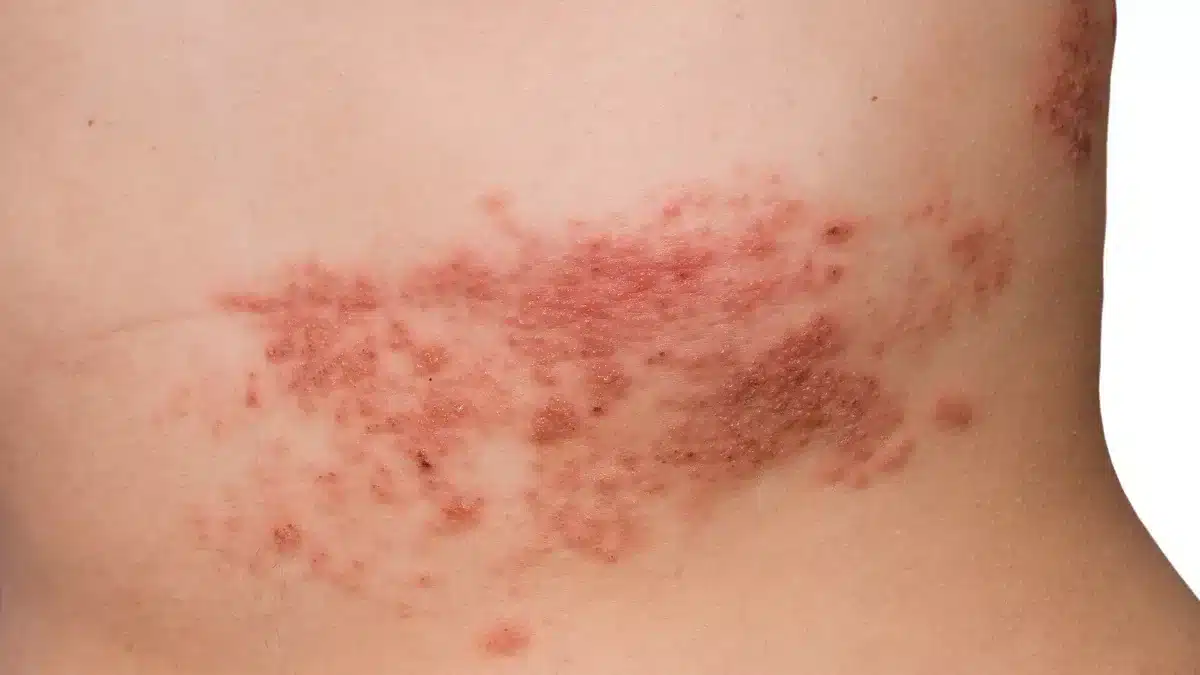
In cases of genital Herpes, the genital area’s skin can undergo inflammation and pain, giving rise to the development of small clusters of blisters.
These blisters, occurring in groups, may rupture, leading to a weeping discharge and scabs during the healing process.
Individuals often encounter symptoms like pain during urination. Itchiness or a burning sensation may also be experienced.
Men typically experience symptoms affecting the penis, foreskin, and scrotum.
While women may experience symptoms in the labia, vagina, and cervix.
Additionally, blisters may emerge in the anal region, on the buttocks, or inner thighs.
Some individuals may detect the onset of an outbreak through a tingling sensation in their genitals or pain in the lower body, hips, or legs.
Symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Headache
- General fatigue
- Muscle pain
- Swollen nodes in the groin area
Subsequent outbreaks are generally less intense.
A suppressed immune system can lead to more severe and prolonged symptoms.
Causes of genital Herpes
Genital Herpes is mainly caused by two types of Herpes Simplex Viruses: HSV-1 and HSV-2.
While HSV-1 is traditionally associated with oral Herpes and cold sores. It can also lead to genital Herpes through oral-genital contact.
HSV-2 is the common culprit for genital Herpes. It is usually transmitted through sexual contact.
Transmission

The most common mode of transmission is through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual during intimate activities.
This includes vaginal, anal, or oral sexual activity.
The virus can also transmitted even if the infected person is not displaying symptoms or experiencing an outbreak.
Transmission is more likely during active outbreaks when the virus is present in higher concentrations.
Diagnosis of genital Herpes
Diagnosing genital Herpes typically involves a combination of medical history review and laboratory tests.
Several diagnostic tests are commonly used:
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR is a molecular technique that magnifies and identifies the genetic material of the Herpes virus.
This highly sensitive method aids in confirming the diagnosis by identifying the viral DNA or RNA.
Clinical examination
Healthcare providers conduct a thorough physical examination.
It will assess the presence of visible symptoms such as sores, blisters, or lesions.
Viral culture
A sample is taken from a Herpes sore or blister on the penis.
The collected material is cultured to identify the presence of the virus.
Blood tests
Blood tests are designed to screen for the presence of antibodies against the HSV.
These antibodies are detected in the blood, indicating either a current or past infection.
Treatment options
While there is no cure for genital Herpes, several treatment options are available.
They aid in managing symptoms and minimize the risk of transmission.
Antiviral medications

Antiviral medications like Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Famciclovir are commonly prescribed to treat genital Herpes.
These medications can help control symptoms and reduce the duration of virus outbreaks and the risk of transmission.
It is essential to start treatment as early as possible, preferably when symptoms first appear.
Pain relief
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers like Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen may be recommended.
These drugs may be used to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with genital Herpes outbreaks.
Topical treatments
Topical antiviral creams may be prescribed to relieve itching and discomfort during outbreaks.
However, these creams are generally less effective than oral antiviral medications.
Prevention of genital Herpes
Preventing the transmission of genital Herpes is a crucial aspect of managing this common STI.
Here are key measures to prevent the spread of genital Herpes:
Safe sexual practices
Always use protection or barrier methods such as condoms or dental dams correctly during intimate activities.
This can prevent Herpes transmission.
Open communication

Engage in open and honest communication with couples about sexual health and history.
Discussing STIs can create a more informed and responsible approach to preventing the spread of genital Herpes.
Regular testing
Routine screenings and testing for Sexually Transmitted Infections, including Herpes, are crucial for early detection and treatment.
Knowing one’s STI status allows for informed decision-making and preventive actions.
Avoiding sexual contact during outbreaks
Avoiding sexual activity during active outbreaks and using caution when symptoms are present.
This can significantly help in reducing the risk of transmission.
Education and awareness
Increasing awareness about genital Herpes, its transmission, and preventive measures is essential.
Education fosters a proactive approach to prevention.
Antiviral suppressive therapy
For individuals with recurrent symptoms or frequent viral shedding, antiviral suppressive therapy may be recommended.
This involves taking antiviral medications daily to reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. It also helps in lowering the risk of transmission.
Psychological Impact
Genital Herpes can have a significant psychological impact on individuals.
It may affect their emotional well-being, and they may have feelings of embarrassment, shame, anger, or even depression.
These emotional responses are a natural part of the adjustment process.
As individuals become more informed about the condition and learn about available treatments, the intensity of these emotions tends to subside.
Receiving help from support groups, friends, or mental health professionals is essential.
It will help address the emotional aspects of living with genital Herpes.
Conclusion
Genital Herpes is caused by the HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus). This virus is highly contagious.
It is of two types: HSV-1 and HSV-2. Type 2 is more commonly linked to genital Herpes.
The symptoms may include inflammation, painful blisters, itching, and burning sensations.
Antiviral drugs like Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Famciclovir prove effective in managing symptoms and reducing transmission risk.
Prevention strategies include safe sexual practices, regular testing, and the use of antiviral suppressive therapy for recurrent symptoms.
Genital Herpes can also have a psychological impact, inducing emotions such as embarrassment, shame, and depression.
With informed decisions and support, individuals can navigate the complexities of living with the virus.
Frequently Asked Questions
What can cause genital Herpes?
Genital Herpes is primarily caused by the HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus). HSV-2 type is the main culprit. Transmission occurs through direct skin-to-skin contact during intimate activities. The virus is highly contagious, even in the absence of visible symptoms.
What are the symptoms of genital Herpes?
Genital Herpes symptoms include inflammation, painful blisters, and itching or burning sensations in the genital region. Women may experience pain during urination. Outbreaks can also affect the anal region, buttocks, or inner thighs. Initial outbreaks are often more severe, accompanied by fever and muscle pain.
How to treat genital Herpes?
Genital Herpes has no cure. However, antiviral medicines such as Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Famciclovir can manage symptoms and reduce transmission risk. Early initiation of treatment during outbreaks is crucial. Pain relievers and topical treatments may alleviate discomfort.
What steps can be taken to prevent genital Herpes?
Preventing genital Herpes involves using protection or barrier methods like condoms and having open communication with sexual partners about STIs. Regular testing and avoiding sexual activity during outbreaks are crucial. Antiviral suppressive therapy may be recommended for recurrent cases.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trustworthy.