Birth Control Options: Types, Methods, Safety, Effectiveness, & Side Effects
Birth control options, or contraception, are effective methods to prevent pregnancy worldwide.
According to the United Nations 2019 report, around 966 million people use some method of contraception, where approximately 151 million solely rely on birth control pills.
Amid the array of numerous types of birth control methods, finding the right one for you can be highly challenging due to the variety of options.
Some birth control options act as barriers between the cervix and the egg, while others may release the hormones to change the optimal condition required for fertilization.
Further, a few birth controls are used at the time of sexual intercourse to provide temporary protection, whereas others can provide a permanent solution.
This comprehensive article will elaborate on the different birth control methods to prevent pregnancy and their efficacy in reducing the risks of STDs.
Barrier methods
Barrier methods block the entry of sperm into the female uterus.
They can be used at the time of having sexual intercourse.
The different barrier methods can be understood in the following ways:
Condoms

Condoms are effective methods of contraception made from thin latex, plastic, or lambskin that can prevent pregnancy.
There are two types of condoms, i.e., condoms worn on the penis by men and condoms worn inside the vagina by women.
They create a physical barrier and prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
Further, as per the NCBI, condoms can also protect against the following STDs:
- Gonorrhea: Up to 90%
- Chlamydia: Up to 50% to 90%
- HIV and Hepatitis B: Around 90%
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV): 50% to 90%
- Herpes Simplex Virus: Around 10% to 50%
However, in some cases, condoms may break, rip, or tear and become unusable.
The factors that can increase the chances of tearing the condom include heat, oils, sun, and chemicals.
Spermicide
Spermicide is a gel or cream containing chemicals that stop sperm so that they cannot reach the egg.
It is 70% effective and can prevent pregnancy.
Spermicide comes in various forms, like cream, gel, foam, and film.
There are also prescription-based vaginal gels that make it hard for sperm to swim and reach the egg.
It is 86% to 93% effective.
Spermicide or vaginal gels are used at least 10 to 15 minutes before sexual intercourse.
They can work for about an hour before reapplying.
However, it cannot prevent STDs rather, it can elevate the risk of acquiring STDs by irritating the vagina and making it easy to acquire an infection.
Cervical cap
The cervical cap is a thimble-shaped cup that blocks the cervix.
It is usually coated with spermicide to damage sperm.
It is 86% effective in preventing pregnancy in women who have never given birth.
A pelvic examination is needed to find the correct measurement of cervical caps.
Diaphragm
Diaphragms are up to 87% effective if used correctly.
A vaginal diaphragm is a small dome-shaped flexible, and reusable placed inside the vagina to prevent pregnancy.
It prevents sperm from reaching the uterus by blocking the cervix. However, it does not protect against STDs.
The diaphragms are available in different sizes and need a pelvic examination for the correct measurement.
Vaginal sponge
A vaginal sponge is a small device that contains spermicide and acts as a barrier between sperm and the female cervix.
It is placed in the vagina and covers the cervix. It needs to be wet with water to activate all spermicides.
The vaginal sponge is effective between 84% to 91% if used correctly.
The sponge contains enough spermicide that can last for up to 24 hours.
Hormonal contraception
Hormonal birth control options prevent ovulation, which is the release of eggs, or change the conditions in the female cervix and vagina.
The various hormonal contraception includes the following birth control options:
Combination pills
Birth control, or combination oral pills, are hormonal birth control methods used to prevent pregnancy.
They have hormones, such as Estrogen and Progestin, which are responsible for the menstrual cycle in women.

Looking for a reliable and convenient solution for confident family planning?
Get the best oral contraceptives from WowRx now
YasminFemilonBirth control pills prevent pregnancy in the following ways:
- Estrogen in birth control pills prevents ovaries from releasing an egg
- Progestin thickens the cervical mucus to make it harder for sperm to reach the egg
- Progestin results in the thinning of the uterine lining (endometrium) to prevent implantation
Some common side effects of birth control pills are as follows:
- Headaches
- Breast tenderness
- Bleeding between periods or breakthrough bleeding
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight gain
- Mood swings
Women who take oral contraceptives have a 30% less risk of developing Endometrial Cancer and may further decline if used for a longer time.
Mini pills
The other form of contraceptive pill, i.e., minipill, contains Progestin only.
It thickens the cervical mucus and makes it harder for sperm to reach the egg.
Further, it can thin the uterus lining and help in lighter periods.
Birth control patch
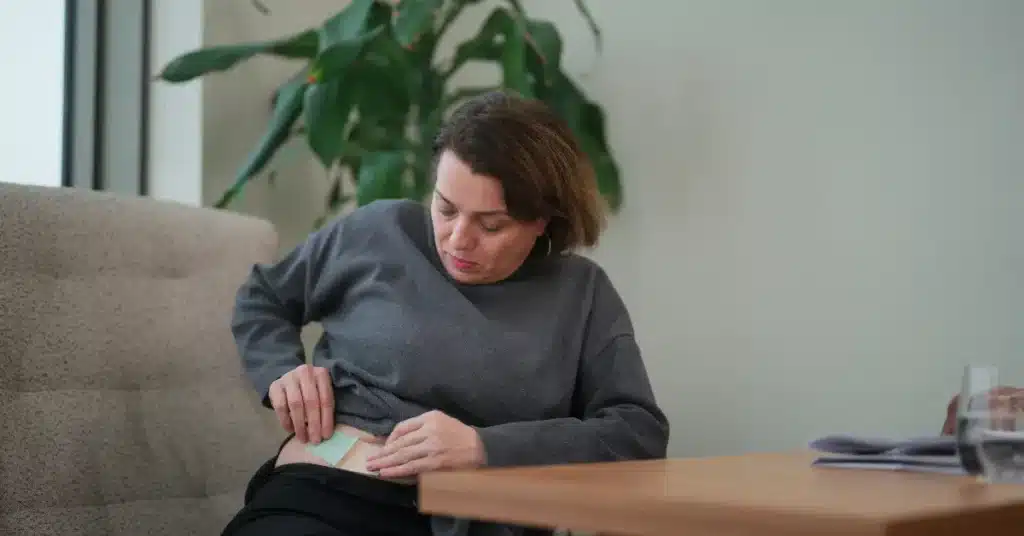

A birth control patch is a type of contraception that contains hormones, i.e., Estrogen and Progestin, and is applied once a week.
The birth control patch can prevent pregnancy in the following ways:
- Prevents ovulation by releasing hormones into the bloodstream
- Thickens cervical mucus and prevents sperm from reaching the egg
The birth control patch is directly applied to the skin and steadily releases hormones into the bloodstream.
The birth control patch can be applied on the lower abdomen, back, upper arms, and buttocks.
Vaginal rings
Vaginal rings are small and flexible rings worn inside the female vagina.
The rings release Estrogen and Progestin through the vaginal lining into the body.
Estrogen prevents ovulation, whereas Progestin changes the cervical mucus.
It is worn for up to three weeks and is removed in the fourth week for bleeding to occur.
Birth control shots
Birth control shot is an injectible birth control method for women and needs to be provided every twelve weeks.
It has an effectiveness of 99% if used correctly.
It is injected into the arms or buttocks and contains hormones.
The shot can impact ovulation and thicken the cervical mucus to prevent pregnancy.
Birth control implants
A birth control implant is a rod-shaped device inserted inside the skin of the upper and inner arm by a healthcare practitioner.
The implant is about 1.6 inches or 4 cm long and flexible.
It releases Progestin into the bloodstream for up to three years and prevents pregnancy.
It prevents ovulation and changes the cervical mucus, preventing sperm from reaching the egg.
Also, Progestin thins the uterus lining and declines the chances of implantation.
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
IUD is a reliable and reversible birth control option and can prevent pregnancy for up to 10 years.
These devices are T-shaped and are inserted into the uterus. The efficacy of IUDs is almost 100%. It can also be reversed if you want to get pregnant in the future.
There are two types of IUDs:
- Copper IUD: The Copped IUD prevents sperm from reaching the egg through the vagina and uterus
- Hormonal IUD: Hormonal IUDs make cervical mucus thicker. It also thins the uterus lining and makes the period lighter
Emergency contraceptive method
Emergency contraceptives are used in case of unprotected sex or if birth control fails.
It includes the following methods:
Morning-after-pill
Emergency contraception is used within five days of being involved in unprotected sex.
This birth control method is more effective if pills are taken within three days of sex.
These pills delay ovulation and hence prevent pregnancy.
IUD
The IUD method is also effective as an emergency contraception.
It can thicken the cervical mucus and thin the uterus lining, making periods lighter.
Other methods
The other birth control option includes ways to prevent pregnancy.
It includes the following methods:
Cervical mucous method
This method involves analyzing the vaginal discharge and avoiding sexual intercourse by predicting the most fertile days for pregnancy.
The hormones, i.e., Estrogen and Progestin, can control the cervical mucus.
Through this method, people can keep a record of their ovulation cycle and avoid sexual intercourse during those times.
A brief chart to differentiate between fertile and non-fertile cervical mucus is as follows:
| Aspect | Appearance | Sensation |
|---|---|---|
| Lowest fertility | Nothing observed | Dry, rough, itchy, or no sensation |
| Low fertility | No observation | Damp sensation |
| Intermediate fertility | Thick, creamy, whitish, or yellowing, elastic and sticky mucus | Damp |
| High fertility | Watery, elastic, reddish, or transparent mucus | Wet, smooth, and slippery |
Abstinence

Sexual abstinence is a 100% effective method to prevent pregnancy.
It can also protect against the STDs by abstaining from sexual intercourse.
Sterilization
People can also use the following surgical birth control options:
Salpingectomy
Salpingectomy includes the permanent surgical removal of one or both fallopian tubes.
This type of surgical method is 100% effective in preventing pregnancy.
Thus, it prevents the movement of the egg to the uterus. Further, it prevents the movement of sperm to the actual site for fertilization, i.e., the fallopian tube.
Tubal ligation
This process of birth control method is almost similar to the salpingectomy. However, in this method, fallopian tubes are not completely removed.
Rather, they are blocked or cut. People after surgery can have normal periods and normal sex.