Ultimate Guide to Genetic Hair Loss
Androgenetic Alopecia, or Genetic Hair loss, runs in families and is a widespread cause of hair loss.
Genes have a significant role in defining how much hair loss you may experience as you age.
Many other factors may cause balding, such as stress, diet, and certain medicines.
According to a 2017 study, out of around 950 patients, Alopecia was prevalent in 67.1 % of men and 23.9% of women.
Although there is no cure for this condition, there are specific ways by which you can slow down the thinning of your hair.
The following article discusses types of genetic hair loss, its symptoms, and treatment options available.
Genetic hair loss occurs in a predictable pattern commonly known as Male and Female Pattern Baldness.
Male Pattern Baldness
As per the US National Library of Medicine (NLM), more than 50% of men over 50 will be affected by this condition to some extent.
Pattern Baldness can begin in the teenage years but is more common in adults.
Men who have close relatives with genetic hair loss are at more risk.
There is an even greater risk if the relatives are from the maternal side of the family.
The genetic component of pattern baldness in males is still unclear.
Still, it is thought to be polygenic, which means that more than one gene is responsible for it.
A large study with 12,806 men of European ancestry states those with the AR gene had more than twice the risk of developing hair loss than those without the gene.
However, this is not the only gene that influences baldness.
According to a 2017 review, 63 genes may be involved in Male Pattern Baldness, with only six found on the “X” chromosome.
Female Pattern Baldness
For most women, hair loss starts in mid-life, once she is in her 40s, 50s, or 60s. But it may start sooner for some.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), Female Pattern Hair loss is a progressive condition. Women with genetic hair loss may continue to lose hair.
It can progress to widespread thinning if you do not get the treatment.
Like Male Pattern Baldness, hair loss in females could be the result of genetic inheritance.
It can happen due to the genes of your father or mother or, in some cases, both.
The genes involved are still widely unknown, but like hair loss in men, it involves more than one gene.
As per NCBI data, Female pattern baldness affects 40% of women by age 50.
Symptoms of Genetic Hair loss
Depending on the cause, hair fall can occur in different ways. It can be sudden or gradual, affecting your scalp or the whole body.
For men, genetic hair fall starts as a recession, which is M-shaped at the front of your scalp and often begins in your 20s or 30s.
As time passes, a circular region located at the back of the head, known as the vertex, tends to experience thinning and an increase in size.
Gradually, the hair in this area becomes finer, shorter, and less dense, creating a U-shaped (or horseshoe) pattern of hair loss along the sides of the head.
This is accompanied by a bald spot at the back of the head.
About 80% of males experience Pattern Baldness by age 80.
As per experts at Harvard, women often experience hair loss after menopause in the Ludwig pattern, a gradual recession along the part of their hair.
But, like men, hereditary hair loss in females does not make them completely bald. Your hair parting may grow wider. Hair near your temple may recede.
Nearly half of women may experience genetic hair loss by age 80.
Ludwig Pattern is a method of classifying female pattern baldness and ranges from stages I to III.
How do I know if I have Genetic Hair Loss?
A typical diagnosis of genetic hair fall does not require any test.
Doctors can diagnose by hair loss pattern and a family history of a similar type of hair loss.
However, your doctor may recommend some tests to rule out other causes of hair loss, which may include,
- Medical History: Your doctor will collect your medical history, including family history, recent illnesses, medications, and life changes linked to hair loss.
- Physical Examination: They’ll examine your scalp and hair closely, often using magnification to assess the extent and pattern of hair loss.
- Pull Test: In some cases, they may gently pull hairs from different areas to gauge hair loss severity.
- Scalp Biopsy: If the cause remains unclear, a scalp biopsy may be done to examine scalp skin under a microscope.
- Blood Tests: Checking for underlying medical conditions or hormonal imbalances using blood tests like thyroid, iron, and hormone levels.
- Phototrichogram or Trichoscopy: Non-invasive techniques, including specialized equipment, help analyze hair and scalp conditions.
Depending on the suspected cause, other tests like fungal cultures, hair shaft analysis, or imaging studies may be ordered.
Treatments for Genetic Hair Loss
Hereditary hair loss does not have a cure.
But there are a lot of treatments available that can help one manage the condition effectively.
Here are some ways to address Androgenetic Alopecia:
Topical medications
Doctors generally prescribe topical medicines like Minoxidil, the first line of treatment.
Topical Minoxidil, including foams and solutions, comes in various forms and is applied directly to the scalp.
Minoxidil promotes hair growth by extending the hair growth cycle and increasing hair follicle size.
It’s effective for both Male and Female Pattern Baldness.
However, results vary, and continuous use is typically required to maintain benefits. Side effects may include scalp irritation or increased hair shedding initially.
Oral medications
Medicines like Finasteride are effective for treating hair fall in men.
Finasteride is an oral medication primarily given for Male pattern baldness.
It works by reducing dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels, a hormone linked to hair loss in men.
Finasteride can slow down hair loss, promote regrowth, and is generally well-tolerated but is not approved for women.
Regular medical supervision is recommended when taking Finasteride.
Lifestyle changes
Including healthy lifestyle habits can help your hair health.
Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, getting enough sleep, and lowering stress benefit your overall health and your hair.
To know more about nutrient supplements to overcome vitamin deficiency, you can read Check out the Best Vitamins for Hair Growth – Complete Guide.
Hair transplantation surgery
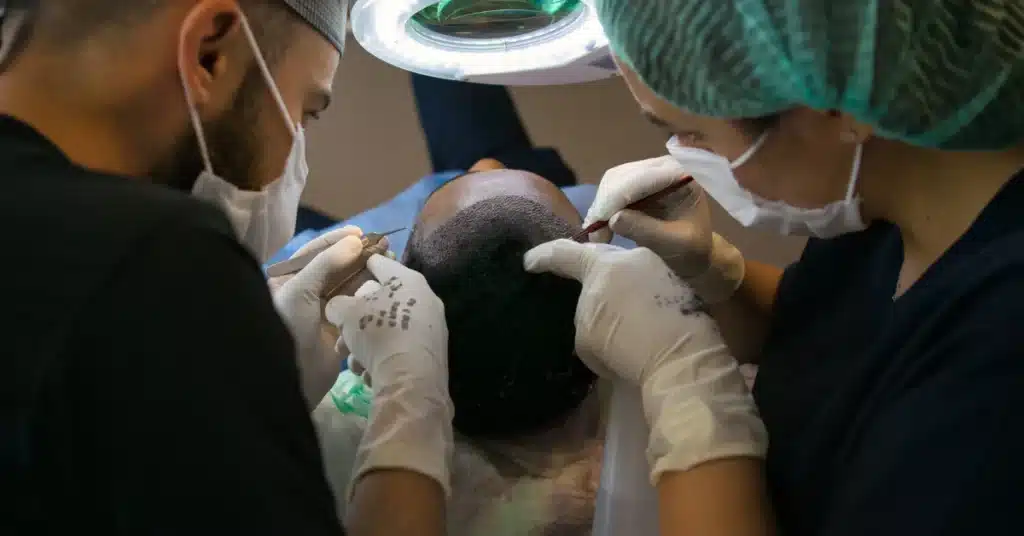
Follicular unit extraction and transplantation surgeries move hair follicles from one part of your scalp to balding areas.
Red light therapy (Laser therapy)
Laser therapy may help improve hair density if you have genetic hair loss or hair loss from chemotherapy.
However, more research is required to determine the effectiveness of this treatment.
It is necessary to check with your doctor and decide the best course of treatment.
Hairstyles
If your hair loss is limited, you can pull it off with the right haircut or hairstyle.
Ask your hair stylist for a cut to make your hair look fuller.
Wigs
Hairpieces or Wigs can mask hair loss, receding hairlines, and total baldness.
Choose the colors, styles, and textures that resemble your natural hair for a more natural appearance. Professional wig stylists can assist in styling and fitting wigs for a more natural finish.
Weaves
Wigs sewn in your hair are known as weaves.
They will work for you with enough hair to sew in the weave.
Weaves always stay in place, even when swimming, showering, or sleeping.
Conclusion
Genetic hair loss, often referred to as male and female pattern baldness, is a common and complex condition influenced by a combination of genetics and hormones.
While it cannot be completely prevented, various treatments are available to manage and slow down the progression of hair loss.
Understanding the genetic factors behind it is crucial in developing effective interventions and ultimately helping individuals maintain healthy and vibrant hair.
As ongoing research continues to shed light on the intricacies of genetic hair loss, hope remains for more advanced and personalized treatments in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is hair loss genetic?
Genes are one of the major factors responsible for hair loss. But it can also occur due to hormonal changes, stress, chemotherapy, nutrition, etc. Check with your doctor to determine the cause of your hair fall.
How to tell if hair loss is genetic or stress?
Doctors identify Genetic pattern baldness by both the pattern of hair loss and the history of other family members with a similar type of hair loss. Your symptoms may differ if it is caused by stress. Check with your doctor, as they may recommend some tests.
Can genetic hair loss be stopped?
There is no cure for genetic hair fall, but medicines like Minoxidil and Finasteride can help you slow it down. Other treatments, such as hair transplant or laser therapy, can help you stop hair loss. Consult a doctor for the best course of treatment.
At what age does genetic hair loss start?
Hereditary hair loss can affect men in their teenage years but is more common in adults. Genetic hair loss in females can make hair shedding begin in their 40s. It becomes more noticeable at 50 and more after menopause.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trustworthy.






