Uncovering the Causes of Alopecia Areata
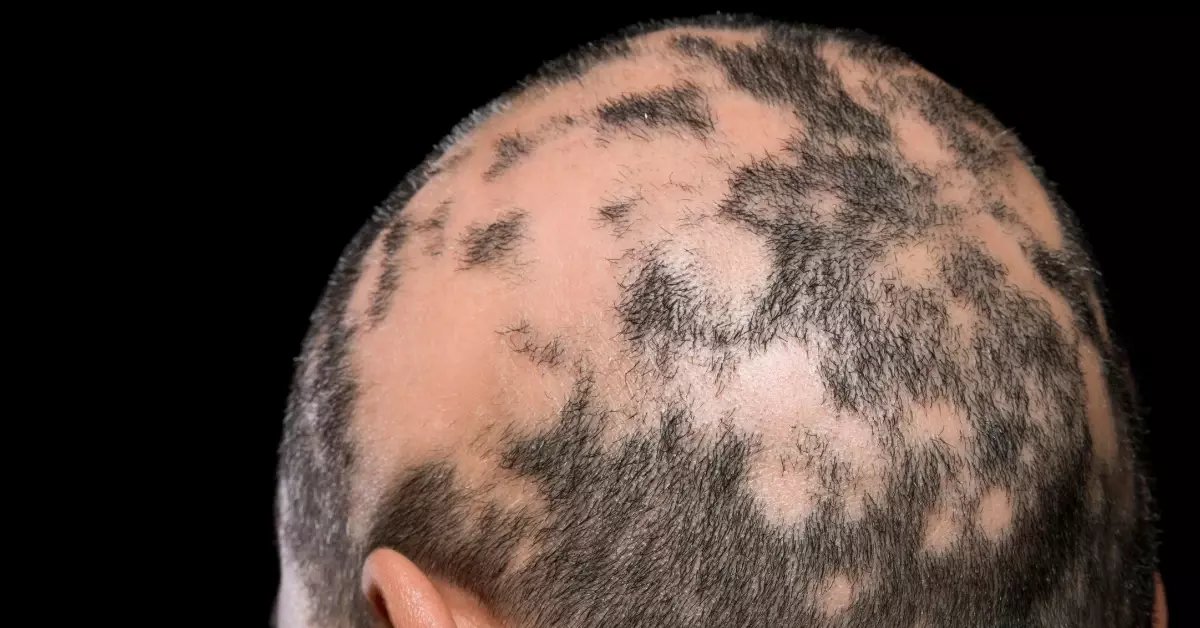
Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss in patches.
Hair loss is due to an immune system attack on the hair follicles.
A study by Fricke and Miteva has shown that 2% of Areata affects 2% of the worldwide population.
The causes of Alopecia Areata are complex and still under research.
Experts claim that a combination of genetic, environmental, and dietary factors triggers hair fall.
But, the immune response does not damage the hair follicles, and hair can regrow on treatment.
Continue reading to know more about the causes and risk factors that can lead to Alopecia Areata.
Genes
Areata is an autoimmune disorder that generally runs in families, says a study by Simkaou, Butcher, et al.
It is a polygenic disease caused due to interactions of more than one gene.
Genetic perspectives of Areata are studied by Biran et al.
The study stated that genes responsible for Areata belong to the family called Human Leukocytes Antigens (HLAs).
The HLA complex works to help the immune system distinguish the bodies from proteins made by foreign bodies.
Each gene of the complex has several variations.
This allows the immune system to react to a wide range of foreign proteins.
Some of these HLA genes are responsible for the immune system’s attack on the hair follicles.
Besides HLA, other genes are also involved in inflammation and have been associated with Alopecia Areata.
Environment
In support of evidence, it is a fact that environmental triggers can cause autoimmune disorders.
The factors such as chronic stress, hormones, sudden shocks, and disease conditions can stimulate the immune system to cause inflammation in hair follicles.
Other factors include allergies, chemicals, seasonal changes, and skin injury, if any.
Extreme stress can trigger an immunological response by overproduction of free radicals.
A 2015 study conducted in China found that Alopecia Areata was triggered in people with dust mite allergies.
Physical injuries such as cuts, scrapes, and other types of damage on the scalp can also result in patchy hair loss.
Despite all of this, these triggers only cause temporary damage to the scalp. This means that hair loss is temporary and hair regrowth is possible.
Vitamin D deficiency

Dietary causes of Alopecia Areata include a vitamin D deficiency.
A 2020 study states that vitamin D plays an important role in immune health.
In deficient amounts, vitamin D can be linked to several immunological disorders, including Alopecia Areata.
Keratinocytes in the skin metabolize vitamin D.
These Keratinocytes are also responsible for processing keratin found in nails, hair, and skin.
In cases of vitamin D deficiency, Keratinocytes in hair follicles are unable to prevent hair loss leading to Alopecia Areata.
Medications
Some of the medications used as therapy for other conditions can also stimulate Areata in the body.
These medicines promote immune response, which can lead to inflammation in hair follicles to cause hair loss.
The medicines include,
Nivolumab
Nivolumab belongs to the medical class of Monoclonal antibodies which are prescribed to cancer patients.
Studies have shown that few cancer patients who took Nivolumab have developed Alopecia Areata.
The condition is also called Nivolumab-induced Alopecia areata.
Abacavir
Abacavir is a reverse-transcriptase inhibitor that is prescribed as a treatment for HIV.
Evidence supports that Abacavir can be a cause of a patchy bald scalp. The results have shown patchy hair loss in 5% of patients who received the immunotherapy.
Fluvoxamine
Fluvoxamine is an antidepressant prescribed in patients with mental conditions such as Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, anxiety, and depression.
Studies support the claim that antidepressants like Fluvoxamine can be one of the causes of Alopecia Areata.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune diseases are when the body’s immune system can’t differentiate between its cells and foreign invaders.
Doctors have suggested that there can be a possibility of Alopecia Areata to occur with other autoimmune disorders such as Thyroid or Type 1 Diabetes.
“Autoimmune conditions often travel in packs, so if you have one autoimmune disorder such as thyroid or diabetes, it is not uncommon to have others”
Brooke Jackson, MD, a board-certified Dermatologist and Dermatologic surgeon
Studies have also shown similar results where Type 1 and Type 2 diabetic patients were at an increased risk of Areata.
Even the genetic actions linked with Alopecia Areata have been identified in people with other autoimmune disorders.
It suggests that this disease may share some genetic risk factors.
Who is at risk of developing Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia Areata can occur in people of any gender and race.
The link between specific race and autoimmune disorders is still under study.
There is evidence that most people develop Areata before 30.
On the other hand, causes of Alopecia Areata can put some people at comparatively more risk than others of developing the disorder.
People with a relative suffering from Areata are prone to developing patchy baldness.
Others who may suffer from disorders such as Asthma, Vitiligo, Atopic Dermatitis, Thyroid disease, Down syndrome, and Hay fever can also get Areata.
Conclusion
Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition that results in hair loss due to your immune system attacking the hair follicles.
Although the causes of Alopecia Areata are unknown, it is believed to be a result of genetic and environmental factors.
A dermatologist can help diagnose Alopecia Areata and provide the best treatment options to promote hair growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes Alopecia Areata?
Alopecia Areata can be caused due to factors including genetic and environmental triggers. It is said to run in families and can also result from chronic stress, physical injury, or other autoimmune disorders like Vitiligo or Diabetes.
What causes alopecia areata in a child?
Alopecia Areata in children can be a result of hereditary factors. It usually runs in families and can be a result of genetic reasons.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trustworthy.