Complete Guide to DUPA Hair Loss
Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, commonly known as DUPA, is a subtype of genetic hair loss.
Hair loss due to genetics, formally known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is common in both men and women. It includes two subtypes: Diffuse Patterned Alopecia (DPA) and Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, with DPA being more common.
In DPA, hair thinning starts particularly across the scalp’s front, top, and crown parts. It has a stable, permanent zone and doesn’t spread all across. On the other hand, in Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, there is no stable zone for hair thinning. It happens across the scalp in an unpatterned or without a particular shape.
DUPA affects the frontal, crown, side, and back parts of the scalp and is not very common, occurring in only 2-6% of men. To learn more about DUPA hair loss, read this informative article.
Symptoms of DUPA
DUPA symptoms are similar to common hair loss. If you have Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, you might notice:
Hair thinning

Hair thinning in DUPA occurs gradually, without sudden changes or bald spots on the scalp, but it gives the appearance of sparser hair distribution, thinly scattered over the head.
This symptom can be challenging to notice at first. However, you can pay attention to subtle signs such as a widening hair part or a thinner ponytail, which may indicate the progression of hair thinning.
Miniaturization of hair
This is the prime symptom of Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, where individual hair strands progressively become shorter and thinner until they almost disappear.
DUPA patients experience rapid and widespread thinning across the front, crown, sides, and back of the head, with the majority of hairs undergoing or eventually undergoing miniaturization.
Changes in hair density
DUPA primarily leads to changes in hair density rather than complete baldness, which poses a challenge in identifying it using traditional hair loss patterns.
Unlike other forms of Alopecia, DUPA results in diffuse thinning across the entire scalp, including the back and sides, without a stable permanent zone for hair transplantation. This rapid and widespread thinning, characterized by hair strand miniaturization, progresses faster than other Alopecia types, leading to extensive, patternless hair loss.
Weak and Dry Hair
Weak hair lacks strength, often displaying signs like split ends, extreme dryness, or excessive oiliness. Factors such as sun exposure, chlorine, saltwater, pollution, and heat styling can weaken hair.
Dry hair, on the other hand, appears dull, brittle, and frizzy, leading to breakage due to inadequate moisture retention. Both weak and dry hair can eventually result in breakage and require careful attention and maintenance.
Causes of DUPA hair loss
Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia (DUPA) is typically genetic, but other factors can also contribute to DUPA hair loss. These may include:
Heredity
DUPA is stated as a heredity condition. Meaning if someone in your family has experienced hair problems, you may be at risk as well. While DUPA commonly occurs with aging, it can also affect young men. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Poor dietary habits
A diet that doesn’t provide enough nutrition can be one of the leading causes of hair loss. As stated above, DUPA can be caused by hereditary factors, and poor dietary habits might be a contributing factor too.
Genetic factors can contribute to a deficiency of crucial nutrients like Zinc, which plays a role in maintaining healthy hair. A lack of Zinc may lead to brittle hair, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet and adequate nutrient intake for hair health.
Constant traction
Constant traction, also known as Traction Alopecia, occurs when there is a continuous pulling force on the hair roots. This can result from hairstyles that tightly pull the hair, such as braids, ponytails, or extensions. Over time, this constant pulling can lead to hair loss, including Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, highlighting the importance of gentle hair care practices.
Treatment of Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia
While there is no defined treatment for Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia (DUPA), a hair transplant is not recommended. In a hair transplant, good-quality hair is moved to areas with thin or no hair.
Due to the widespread nature of hair loss in DUPA, including the front, top, and crown, a hair transplant may not be effective. Additionally, the condition may not provide suitable donor hair for the transplant procedure. However, some options still exist for treating DUPA hair loss caused by hereditary factors. It includes:
Minoxidil
Minoxidil, renowned for addressing various hair problems, including Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia (DUPA), promotes hair growth and alleviates hair thinning. This FDA-approved medication is suitable for both men and women experiencing hair loss.
Finasteride
Finasteride, available in both oral and topical forms, may help increase scalp hair. The oral form, FDA-approved and sold under names like Finpecia, Propecia, and Finalo, is commonly used for treatment.
However, the topical form, also in high demand, is preferred for its lower incidence of side effects compared to the oral tablet form.
Platelet-rich plasma
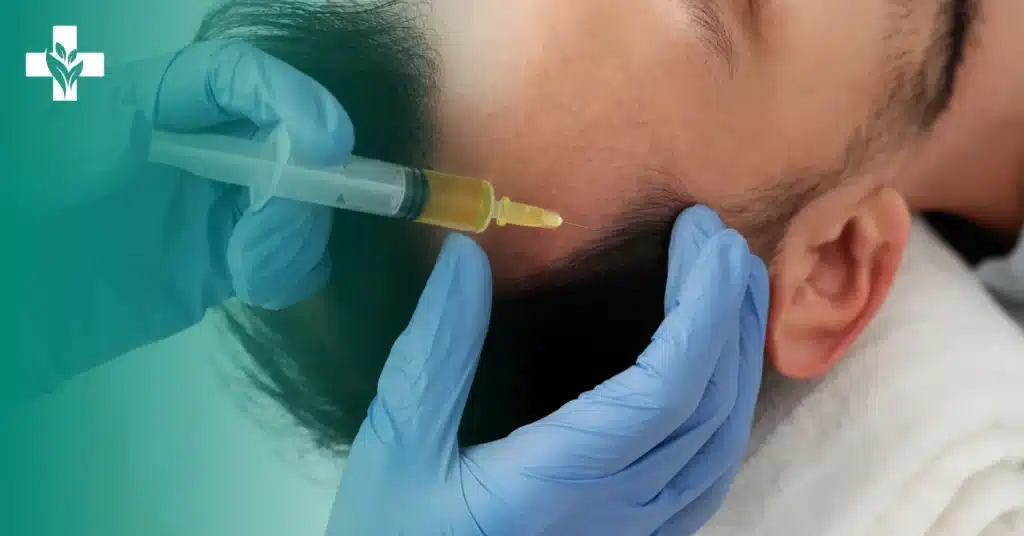
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a popular hair growth and restoration treatment that utilizes platelets, which are approximately five times more concentrated than normal blood. This treatment secretes growth factors that may aid in the treatment of thin hair problems.
Takeaway
Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, commonly known as DUPA, is a type of hair loss caused by genetics, falling under the category of Androgenetic Alopecia. The primary difference lies in DUPA’s unpatterned hair thinning, unlike the more typical patterned thinning seen in Androgenetic Alopecia.
If you have Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia, you may notice low hair density, miniaturization, weak hair, etc.
Heredity is the leading cause of DUPA hair loss. However, constant traction and an unhealthy diet can also be contributing factors.
For DUPA hair loss treatment, a hair transplant is not advised. Topical or oral medications like Minoxidil and Finasteride might be recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is DUPA hair loss?
Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia is a type of hair loss caused by hereditary factors. It is usually not common. It may affect people of any age, sometimes young patients. This type of hair loss is hard to diagnose, and a hair transplant is often not recommended for treatment.
Is DUPA hair loss reversible?
Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia may be treated with certain medications. Your doctor may prescribe you oral or topical medicines like Minoxidil or Finasteride. Platelet-rich plasma may also be used for the treatment of DUPA hair loss.
What causes DUPA hair loss?
Heredity is the leading cause of Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia. If anyone in your family has hair problems, you might have it too. Other factors like an unhealthy diet and constant traction may contribute to DUPA hair loss.
What are the signs of DUPA hair loss?
Hair thinning and miniaturization of hair are the prime DUPA hair loss symptoms. It occurs not only on the front and top of the scalp but also on the back and sides. Also, weak and dry hair can be noticed in patients with Diffuse Unpatterned Alopecia.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trustworthy.






