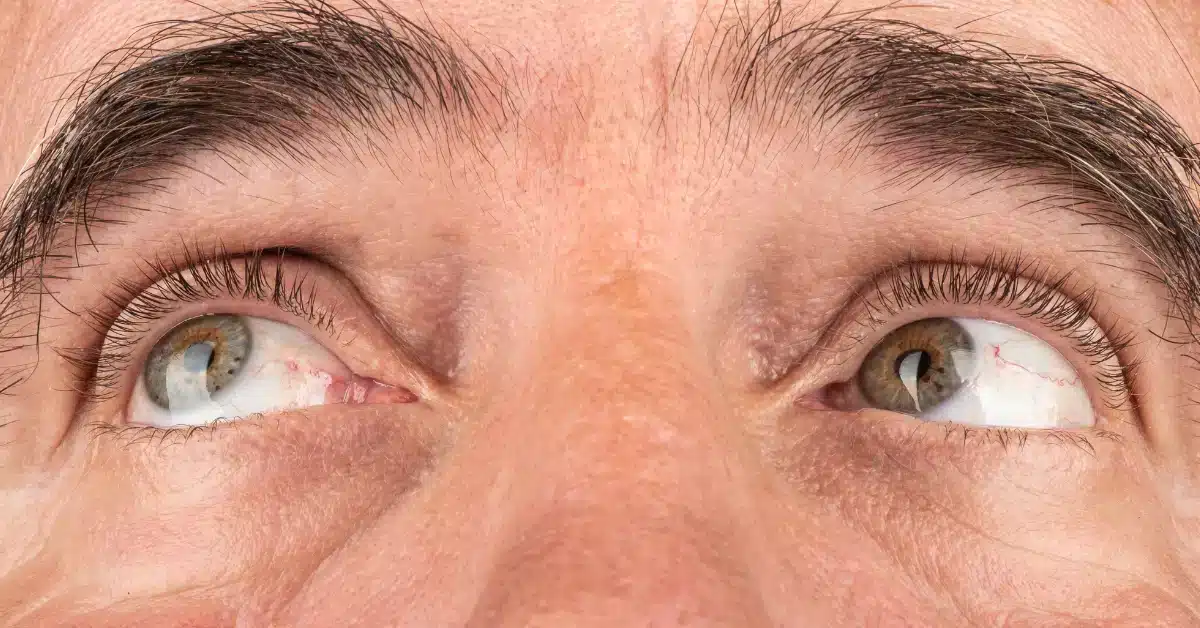
Keratoconus Symptoms: Know the Signs
Keratoconus is a chronic eye condition in which the cornea thins and bulges over time.
It affects both eyes, but in most cases, one eye is more affected than the other.
You may experience blurry or distorted vision if you have it.
However, it is a rare condition. According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, it occurs in approximately one in 2000 people.
This article will help you look out for Keratoconus symptoms and signs if you are facing any vision problems.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of Keratoconus may change as the condition develops.
You may see the signs in one eye in the beginning. But in most cases, Keratoconus affects both eyes.
Although, it might get challenging to see as the condition progresses slowly.
Keratoconus symptoms often start in the early years of life (before 20) and progress until about the age of 40.
Sensitivity to light
Sensitivity to light is another symptom of Keratoconus that can affect your daily life.
Long hours at a computer screen can increase the light sensitivity in patients.
Thus avoid driving, especially at night if you have Keratoconus.
Changes in vision
In keratoconus eyes, the cornea swells and starts to scar.
Due to the scarring, the cornea loses its smoothness and becomes unclear, resulting in distorted and blurry vision.
For some patients, swelling can be sudden, and the condition can worsen quickly.
Early on, there is mild blurriness and slight distortion, which can worsen with time. In rare cases, if left untreated, you may lose vision.
If not treated, in rare cases, you may lose vision completely.
Usually, spectacles help to correct vision problems at early stages. However, if spectacles become impractical, it’s a sign that the condition is progressing.
Astigmatism
Astigmatism occurs when the cornea of the eye has an irregular shape.
Cornea does not bend properly on the retina, causing blurry vision.
Similar to Astigmatism, Keratoconus also has the same symptoms.
In Keratoconus, the cornea bulges outward and has a conical shape. Hence people with Keratoconus also have Astigmatism symptoms.
Myopia

Keratoconus also shows signs of nearsightedness (Myopia).
Myopia is an eye condition in which objects at a farther distance look blurry.
Hence, children with Keratoconus have difficulty looking at a whiteboard and screen projections in the classroom.
When to go to a doctor
Keratoconus often starts in the teen years.
It can generate sudden changes in your vision and may develop through the years.
The changes occur primarily due to Astigmatism and may affect your distant or near vision.
If you see any signs of these vision changes, speak with your doctor.
The condition makes it difficult to see clearly without glasses or contacts.
You may need to change your glasses or contact lens prescriptions more frequently. Also, your contact lenses may not fit properly due to the cornea’s irregular shape.
See your doctor or speak with an eye specialist if you face these situations.
Takeaway

Keratoconus is a chronic and bilateral condition.
Symptoms of Keratoconus include blurry and distorted vision, photophobia (light sensitivity), Astigmatism, and Myopia.
As the condition advances, symptoms of this eye disease get worse.
If the condition is not treated, the patient may lose vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the early stage of Keratoconus?
At the early stage of Keratoconus, your cornea starts to thin and bulge outwards. In the beginning, your vision is slightly compromised and distorted. Your eyes may become sensitive to light, causing problems with night driving.
Can I go blind with Keratoconus?
There is no way to predict how long Keratoconus will progress and how much it will affect the patient. It usually develops slowly till the age of 40. If the progression is rapid, without treatment, it can cause vision loss.
At what age Keratoconus stops?
Keratoconus is a chronic disease that appears between the ages of 10-20. By the age of 40, it usually stops. However, there are several effective treatments available. You can consult a doctor to stop the progression before your vision worsens.
WowRx uses only high-quality sources while writing our articles. Please read our content information policy to know more about how we keep our content reliable and trustworthy.